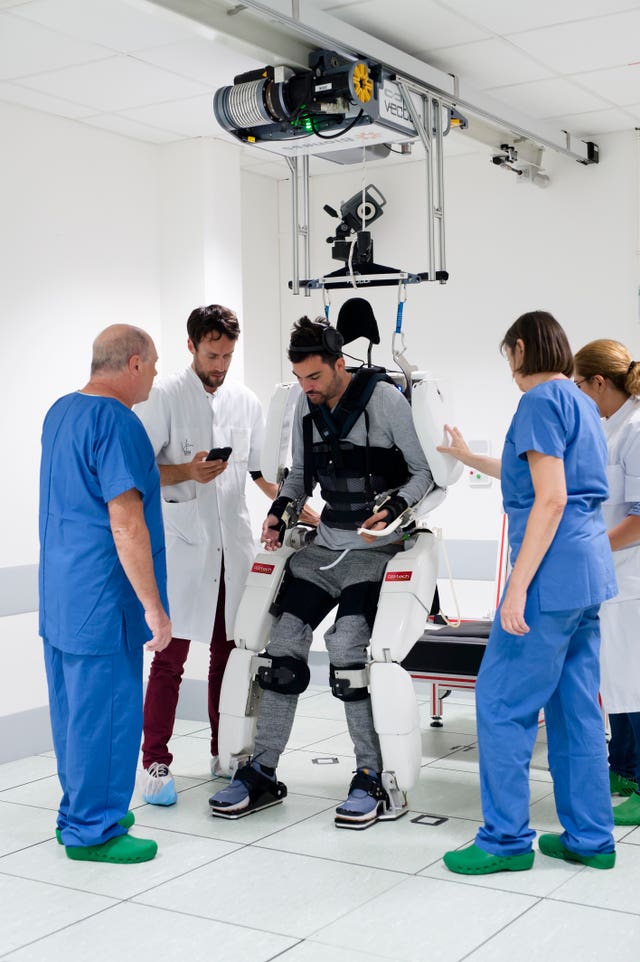
A tetraplegic man in France has been able to walk while wearing an exoskeleton controlled by his brain signals.
The 28-year-old man who is known only as Thibault, said taking his first steps in the suit felt like being the “first man on the Moon”.
The four-limbed robotic system controlled helped Thibault to move his arms and walk using a ceiling-mounted harness for balance.
The whole-body exoskeleton, which is part of a two-year trial by Clinatec and the University of Grenoble, is operated by recording and decoding brain signals.
Thibault was an optician before he fell 15m in an incident at a night club in 2015.
As part of the trial, he had surgery to place two implants on the surface of the brain, covering the parts that control movement.
Sixty-four electrodes on each implant read his brain activity and beam the instructions to a computer.
Software then reads the brainwaves and turns them into instructions to control the exoskeleton.
“It was like [being the] first man on the Moon. I didn’t walk for two years. I forgot what it is to stand, I forgot I was taller than a lot of people in the room,” he said after successfully using the exoskeleton.
A previous patient recruited to the study had to be excluded because a technical problem prevented the brain implants communicating with the algorithm. The implants were removed.
Professor Alim-Louis Benabid of the University of Grenoble, said the exoskeleton used is the first semi-invasive wireless brain-computer system designed for long term use to activate all four limbs.
“Previous brain-computer studies have used more invasive recording devices implanted beneath the outermost membrane of the brain, where they eventually stop working,” he told medical journal The Lancet.
“They have also been connected to wires, limited to creating movement in just one limb, or have focused on restoring movement to patients’ own muscles.”
Prof Tom Shakespeare, of the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, said the exoskeleton is a long way from being a usable clinical possibility.
“A danger of hype always exists in this field.
“Even if ever workable, cost constraints mean that hi-tech options are never going to be available to most people in the world with spinal cord injury,” he said.
